With your urologist
On this page:
Discover our animated video!
Symptoms, risk and screening
Are you over 50 years old, or have you been having urinary problems for some time now? This video is for you! Several diseases can affect your prostate, and it’s important to detect them early. Let’s take a closer look.
Consultation
Meeting with your urologist

An urologist is a doctor specializing in genitourinary system disorders. Like your doctor, your urologist will be interested in your:
- Symptoms
- Family history
- Medical history
Your urologist will probably ask you to retake certain tests and exams that you were already given, but he will also ask you to undergo a number of other tests that will help in determining your diagnosis. It is important to know whether you have prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia:
- A physical examination;
- A digital rectal exam (DRE);
- A PSA test;
- A urine analysis;
- A urine flow test: this test checks to make sure that the bladder and sphincter that is responsible for holding the urine in the bladder is working. For this test, you will need to urinate into a special funnel connected to an instrument that calculates the speed of urination;
- A bladder ultrasound: this ultrasound evaluates the volume of urine remaining in the bladder after urination, and the possible urinary obstruction due to pressure from the prostate;
- A transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) of the prostate;
- A magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate (MRI): Allows visualization of the prostate and possibly cancerous lesions in it;
- A prostate biopsy.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)
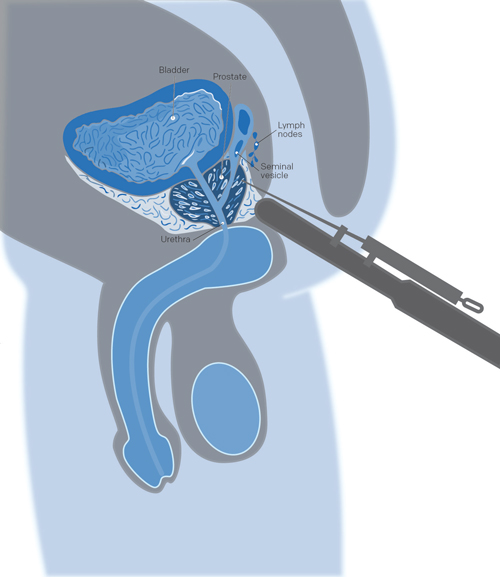
Why? The transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) of the prostate measures the size of the prostate and identifies abnormal regions to be biopsied. It is standard for a biopsy to be performed at the same time as a TRUS which helps guide the biopsy needles during sample collection.
How? For a transrectal ultrasound, you will be asked to lie on your side with your knees brought up to your chest while a lubricated probe is inserted into your rectum. This probe emits sound waves that bounce off the prostate and surrounding tissues back into the sensor. The machine will then show an image of the prostate and the surrounding area on a computer screen. The TRUS does not last longer than a few minutes and does not require any special preparation. It is not painful, but some men find it unpleasant.
Prostate biopsy
Why? Abnormalities detected during a digital rectal exam and a high PSA level often lead to a prostate biopsy. This procedure consists of taking small tissue samples of your prostate in order for the pathologist to examine them under a microscope to determine if they are cancerous or not. If cancer is detected, the pathologist will use the same samples to calculate your Gleason Grade score.
How? A prostate biopsy is usually performed during a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS biopsy). The images taken with the ultrasound help guide a fine needle to the areas selected for sampling. The spring-loaded needle is attached to the ultrasound probe and enters the prostate through the rectum. Usually between 6 – 12 (sometimes more) prostatic tissue samples are obtained and the entire procedure lasts about 10 minutes. A local anesthetic can be used to numb the area and reduce any pain.
Expectations and results
A transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) of the prostate done without a biopsy cannot confirm the presence of cancer. If your urologist detects an abnormality following a TRUS, a biopsy is needed to confirm the prostate cancer diagnosis.
It takes about four weeks to get the biopsy results because the pathologist needs to examine the samples under a microscope before giving his report.
Presence of cancer
- If the pathologist finds cancer in the samples, he will assess the aggressiveness of the cancer by giving it a Gleason grade.
- You will discuss possible treatments with your urologist who may recommend other complementary tests in order to determine how far your cancer has progressed.
Absence of cancer
- The fact that the pathologist did not find any cancer in your samples can be reassuring. However, it is possible that the biopsy needle simply missed the cancerous areas and you do in fact have cancer.
- If your urologist suspects that you have cancer, he may have you do a second transrectal biopsy or another type of prostate biopsy.
- Otherwise, regular prostate checkups, including the PSA test, digital rectal exam (DRE), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be the preferred route.
We are here for you
You have questions or concerns? Don’t hesitate. Contact us at 1-855-899-2873 to discuss with one of our nurses specialized in uro-oncology. They are there to listen, support and answer your questions, and those of your family or your loved ones. It’s simple and free, like all of our other services.
Also take the time to visit each of our pages on this website, as well as our YouTube channel, in order to get familiar with the disease, our expert lectures, our section on available resources, the support that is offered to you, our events and ways to get involved to advance the cause.
Staying Informed
Pages that might interest you
Want to know more? Just click on one of the links below.
The latest PROCURE news that might interest
Every week we publish a blog article. Here are some we have chosen for you.
- Prostate cancer: Did you say zero symptoms?
- Scared stiff of having a prostate biopsy?
- Can an MRI of my prostate replace a biopsy?
The medical content and editorial team at PROCURE
Our team is composed of urologists, nurses certified in uro-oncology with a deep knowledge of prostate cancer and other diseases related to the genitourinary system. Meet our staff by clicking here.
Sources and references
- Prostate Cancer – Understand the disease and its treatments; Fred Saad, MD, FRCSC and Michael McCormack, MD, FRCSC, 4th et 5th editions
- Canadian Cancer Society
- Prostate Cancer Foundation-PCF.org
- National Cancer Institute-USA
- American Cancer Society
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- Prostate Cancer UK
Last medical and editorial review: September 2023
Written by PROCURE. © All rights reserved




